What Is Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP)?

VoIP uses the internet to connect users for audio communication unlike traditional phone lines.
Remember? It was landlines before smartphones.
We ran whenever phones rang, waited in lines to make calls, and most of the time the bills were huge.
But it all changed, when VoIP was discovered. We started to carry a handy device everywhere we go, pick it up and talk to a friend or family who’s in another part of the world.
How did this happen?
I was curious too. So, I gathered a few details about the technological advancements that happened after VoIP was introduced. Stick with me for I’ll be covering all about VoIP in the next 5 mins.
What You’ll Learn?
- What is VoIP: The basics of the technology
- How VoIP differs from traditional phone lines?
- How VoIP works?
- Tips to choose the best VoIP provider
- Bonus: Editor recommendation of the most reliable provider.
Table of Contents
What is VoIP?

VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, is a technology that allows voice conversation and multimedia content delivery via the internet rather than traditional telephone lines. It enables users to make voice calls from a variety of devices, including computers, cellphones, and specialist VoIP phones.
Key Features Of VoIP
- Digital Signal Conversion: VoIP’s key feature is the conversion of analog voice signals into digital data packets for internet transmission. These packets are then reconstructed at the destination to produce the original audio stream.
- Broadband Requirement: VoIP requires a consistent broadband internet connection to perform properly. This implies that customers may make calls from anywhere with internet connectivity, allowing far more flexibility than traditional landline services.
- Unified Communications: VoIP frequently combines many forms of communication such as video calls, instant messaging, and voicemail on a single platform, improving collaboration and productivity for both individuals and enterprises.
The (Quick) History of VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has a long history, starting with early attempts in digital communication and developing to become an essential technology in modern communications. Here is a thorough overview:
Early Developments (1920s – 1970s)
- 1925: The origins of VoIP may be traced back to Bell Laboratories, where AT&T and Western Electric partnered with each other to improve communication technology. This time created the path for future developments in voice communication.
- 1973: The earliest experimental VoIP transmissions took place via ARPANET, an earlier version of the present Internet. In the same year, MIT engineers efficiently transmitted voice data using packet-switching methods, which is a basic cornerstone of VoIP today.
Commercialization and Early Applications (1990s)
- 1991: The first public-domain VoIP program, Speak Freely, was published, allowing users to make phone calls over the Internet. This was an essential phase in making VoIP available to the entire population.
- 1995: VocalTec’s InternetPhone was the first commercial VoIP program, but it required certain software and hardware, making it only accessible to enthusiasts at first.
- 1996: VocalTec launched an extensive VoIP service, but wider acceptance was delayed by limited broadband connectivity and poor call quality compared to traditional phone lines.
Growth and Mainstream Adoption (2000s)
- Early 2000s: As broadband Internet became more readily available, VoIP gained popularity among businesses and consumers. By 2001, VoIP accounted for around 5% of all North American commercial calls.
- 2003: The introduction of Skype changed VoIP by offering free calls between users, significantly increasing public interest and usage. In fact, Skype’s intuitive interface and excellent performance helped it become a household name.
- 2004: The FCC defined VoIP as an information service rather than a telecommunications service, excluding it from many of the laws that apply to traditional telephone companies. This classification helps VoIP companies save huge costs while also encouraging competitiveness in the market.
Technological Advancements (2010s)
- 2010: Mobile VoIP apps, such as Apple’s FaceTime, helped popularize VoIP technology by allowing video chats via cellular networks and Wi-Fi.
- 2018: When Openreach announced plans to phase down ISDN services in the UK, it pushed businesses to take on VoIP solutions as their primary choice of communication.
Current Landscape Of VoIP
Today, VoIP technology has become important for both personal and commercial interactions. It takes up around 60% of new telecommunications connections on a global level. Plus, the ongoing development of cloud-based solutions and mobile apps has strengthened VoIP’s position as a low-cost alternative to traditional telephone systems.
VoIP’s progress strongly relates to larger technological and communication trends, showing how innovations could transform various industries by taking advantage of existing infrastructure, in this case, the Internet to improve connection and lower prices.
How Is VoIP Different From A Traditional Phone System?
There are a lot of differences between how landlines and VoIP-enabled mobile devices work. Traditional phones work based on circuit-switching and VoIP phones work based on packet-switching technology for more efficient communications. In this section, I will walk you through both these technologies to help you understand how VoIP works, very clearly.
Traditional Circuit-Switched Telephony Systems
1. Fundamental Architecture
Traditional telephony systems run on the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), with circuit-switched technology serving as its fundamental architecture.
When a call is begun, the system creates a dedicated physical circuit between the calling parties that stays exclusive until the call is completed. This dedicated circuit provides a continuous bandwidth allotment of 64 kilobits per second (Kbps) in each direction, ensuring a steady and predictable communication channel throughout the session.
2. Operational Mechanism
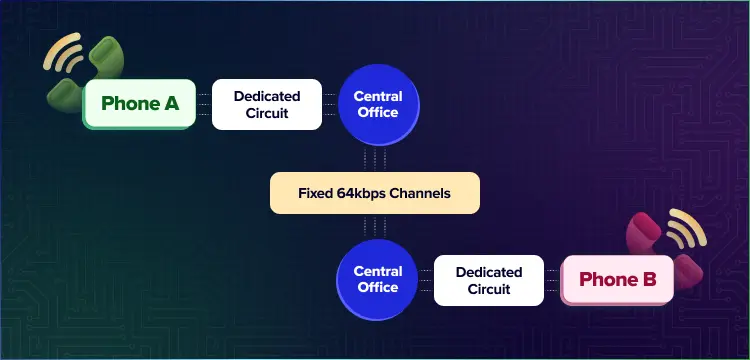
Unlike traditional phone systems, SIP calling apps don’t require physical handsets – when a user initiates a call, signals are sent digitally through the internet rather than through a local telephone exchange. The exchange answers with a dial tone, which verifies the availability of service. Whether the destination is a cell or landline number, the switching equipment in the exchange recognizes it and creates a physical circuit that connects both parties.When you dial the desired number, the switching equipment in the exchange recognizes the destination and creates a physical circuit that connects both parties.
Here, one circuit remains active and devoted to one single call, regardless of whether an active discussion is taking place, until one party quits the connection.
3. Resource Allocation
In conventional telephone systems, resource allocation is fixed. The dedicated circuit uses a preset amount of network resources, specifically the 64 Kbps bandwidth allocation, for the length of the connection.
This allocation remains constantly independent of real speech activity or silent intervals, which may result in poor resource consumption as compared to current telecommunications technologies. The system keeps this dedicated channel until the call is terminated, at which time the resources are released for use by other connections.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Systems
1. Modern Architecture
Voice over Internet Protocol marks an important change in the field of communications, as it uses packet-switched networks rather than traditional circuit-switched systems. This current technique divides speech transmissions into distinct data packets that may transit independently over the network architecture.
The system manages these packets using complex protocols, assuring efficient delivery and reassembly at the destination. This design allows for significantly more flexible and efficient resource use than standard telecommunication systems.
2. Operational Mechanism
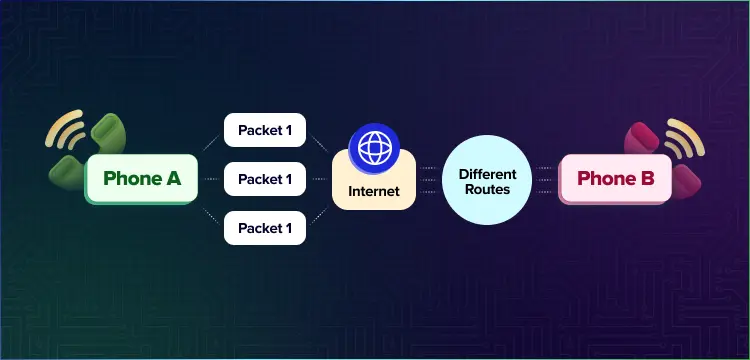
VoIP systems work by transforming analog speech signals into digital data packets that carry important details including source and destination addresses, sequence numbers, and timing data. These packets are sent via the IP network backbone, perhaps taking many paths to their destination.
When these packets arrive, the system reassembles them in the proper order before transforming them to audio signals. The entire procedure is completed with minimum noticeable latency, resulting in smooth communication similar to standard telephone networks.
3. Dynamic Resource Management
Modern voice over internet protocol software stands out for its ability to dynamically allocate resources, unlike older telecommunications systems. Unlike older systems, VoIP only uses network resources when data transfer is required.
During moments of silence, the system can reallocate bandwidth to other active connections, therefore greatly improving network efficiency. This dynamic approach to resource management allows VoIP systems to serve more concurrent users while maintaining high levels of service quality.
4. Quality and Performance Considerations
VoIP systems use complex quality-of-service (QoS) features to provide dependable communication. These approaches include packet prioritizing, jitter buffering, and packet loss masking. While network problems can have an impact on VoIP communication quality, contemporary systems use complex algorithms to ensure call quality on par with traditional telephone networks.
Furthermore, Advanced VoIP software responds to changing network conditions by automatically modifying compression rates and packet sizes in real time for optimal performance.
5. Integration and Scalability
VoIP systems specialize at integrating with various digital communication platforms and services. This integration capability allows for additional services like video conferencing, instant messaging, presence information, and file sharing on the same communication platform.
VoIP systems are more scalable than conventional telephone since they require less extra physical infrastructure to increase services. With VoIP service, organizations can quickly add more users or locations by utilizing existing network infrastructure, resulting in considerable cost savings and increased operational flexibility.
6. Economic Implications
VoIP systems provide significant cost advantages over conventional telephone. VoIP may take advantage of existing data networks, resulting in reduced initial infrastructure expenditures. Operational costs are minimized through improved resource utilization and simpler maintenance requirements.
Long-distance and international calling expenses are much lower since voice traffic is routed via the Internet rather than dedicated phone lines. Furthermore, combining different communication services into a single platform might result in additional cost savings through easier management and decreased hardware needs.
Traditional Phone Lines Vs VoIP: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Phone Service | VoIP |
|---|---|---|
| Call Transmission | Uses dedicated telephone lines and infrastructure | Converts voice to digital data packets and transmits over the internet |
| Call Routing | Routed through telephone company’s network | Can be routed through existing telephone networks or just over the internet |
| Voice Conversion | Analog voice signals transmitted directly | Voice converted to digital data packets |
| Hardware Required | Landline phone or mobile device | Computer, smartphone, or VoIP-enabled device |
| Cost for Calls | Often higher, especially for long-distance and international calls | Generally lower, especially for long-distance and international calls |
| Advanced Features | Limited features like call forwarding, voicemail, etc. | Offers advanced features like call forwarding, voicemail-to-email, video conferencing, etc. |
| Flexibility | Limited to physical location of phone | Portable, can make calls from anywhere with an internet connection |
While traditional telephony systems provided reliable communication for decades, SIP VoIP apps and systems offer tremendous benefits in efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, causing a dramatic shift in telecommunications infrastructure.
Organizations are increasingly using VoIP solutions to benefit from expanded capabilities, more scalability, and lower operating expenses, all while retaining the high-quality communication standards set by traditional phone systems.
How Does VoIP Work?
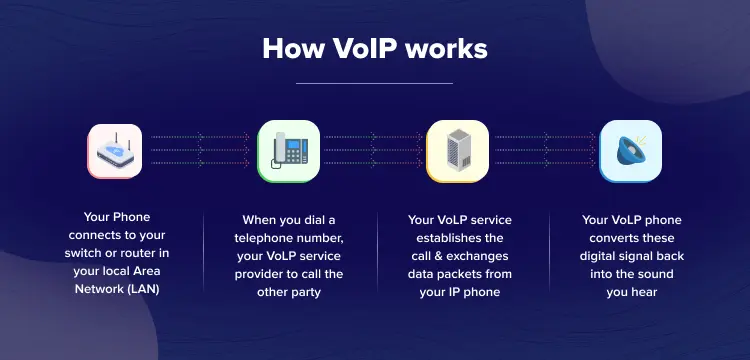
VoIP protocol (Voice over Internet Protocol) is a technology that allows voice communication via the internet rather than traditional phone lines, revolutionizing how we connect. The process consists of numerous processes, including transforming voice signals and transferring them as digital data packets. Here’s a full step-by-step explanation of how VoIP works:
Step1: Initial Registration and Authentication
The VoIP communication process begins with a mandatory registration step in which the endpoint device, whether a hardware IP phone or a software client, establishes its existence within the network.
During the initial setup, the device is assigned a unique Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) and goes through stringent authentication steps. The system validates credentials and sets critical network parameters such IP address assignment, subnet mask setup, and gateway settings.
Furthermore, the registration procedure creates Quality of Service (QoS) characteristics that will influence future communication quality.
The registration protocol uses the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) to organize the procedure in a series of synchronized phases. Initially, the device sends a REGISTER request to the SIP server, which returns an authentication challenge. The gadget then returns encrypted credentials for verification.
After successful validation, the server validates the registration, creating a presence that must be refreshed on a regular basis to remain active in the network. This ongoing registration process keeps the system informed of the device’s availability for incoming communications.
Step 2: Call Establishment and Signaling Protocol
When a user starts a call, the system begins a complicated signaling process that includes the production of a SIP INVITE message. This communication offers complete details about all call participants, including unique identities for both the caller and the intended receiver.
The INVITE message also provides the available codecs, protocols, media transport settings, and a complete session description via the Session Description Protocol (SDP). This information serves as the foundation for constructing the communication channel.
Now, The session negotiation phase follows, in which the system finds the best settings for the next conversation. This process involves establishing compatible codecs between endpoints, assigning adequate bandwidth resources, choosing the most efficient network path, implementing essential security procedures, and selecting acceptable media transport protocols. The negotiation guarantees that both endpoints may interact successfully within the specified boundaries.
Step 3: Audio Processing and Digital Conversion
The evolution of voice communication begins with the analog-to-digital conversion process, which involves multiple complex procedures to turn human voice into digital data.
To maintain appropriate speech quality, the system samples the analog voice stream at a rate of around 8,000 samples per second. These samples are broken down into discrete values and encoded using Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). The system then temporarily saves these digital samples in a buffer for further processing.
Before transmission, the digital signal is extensively processed to improve quality and efficiency. This includes powerful echo cancellation algorithms to remove undesired auditory feedback, complex noise reduction techniques to increase clarity, and Voice Activity Detection (VAD) to distinguish between periods of speech and quiet.
The technology also generates comfort noise during silent intervals and uses automated gain management to keep volume levels consistent throughout the discussion.
Step 4: Data Compression and Packet Formation
The effectiveness of VoIP communication is highly dependent on the codec implementation approach. The system picks appropriate codecs depending on a variety of parameters, including audio quality requirements, available network bandwidth, current network circumstances, and endpoint processing capabilities.
Common codec options include G.711, which works at 64 Kbps without compression, G.729, which compresses data to 8 Kbps, and Opus, which uses variable bitrate encoding to provide maximum quality and efficiency.
The packet creation process prepares voice data for transmission over an IP network. Each packet comprises a 12-byte Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) header that carries critical information such as sequence numbers, timestamps, and synchronization source identities.
The packet also contains an 8-byte User Datagram Protocol (UDP) header and the required IP address information. This organized technique makes sure that packets are properly routed and reconstructed at their destination.
Step 5: Network Transmission and Quality Management
In order to ensure that voice packets are delivered reliably, extensive network management methods are used throughout the transmission phase. The system uses many Quality of Service (QoS) methods to favor voice traffic over less time-sensitive data.
This comprises techniques such as packet priority, traffic shaping, and bandwidth allocation. The network architecture routes packets over several pathways, picking the best route based on current network conditions and congestion levels.
Step 6: Reception and Signal Reconstruction
At the receiving end, the system uses complex methods to rebuild the original voice signal. This includes collecting incoming packets, mitigating any jitter using adaptive buffering methods, and dealing with packet loss using concealment algorithms. The system must reorganize packets that come out of order owing to network routing differences.
Finally, the digital data is converted back to analog signals using a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC), which produces audible speech output via the recipient’s device.
Step 7: Call Termination and Resource Management
The end of a VoIP exchange initiates an orderly termination method that ensures effective cleaning of assigned resources. When both parties terminate the call, the system sends a sequence of SIP messages to politely end the session.
This step includes terminating RTP streams, freeing allocated bandwidth, and updating presence information in the registration server. The system also gathers and saves important call data and quality indicators for system improvement and troubleshooting.
Breaking Down VoIP: Advantages & Disadvantages
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology has influenced how we interact, providing various benefits but also posing challenges. Here are three primary benefits and drawbacks of VoIP in detail.
Advantages of VoIP

1️⃣ Saves a lot of money
Lower Call expenses: VoIP considerably lowers communication expenses, particularly for long-distance and international calls. Traditional phone services can be expensive, but SIP VoIP software allows users to make calls at local rates or even for free to other VoIP users, dramatically reducing communication costs. Many internet service providers incorporate VoIP services as part of their broadband bundles, which reduces expenses for both individuals and enterprises.
No Need for Additional Hardware: Unlike traditional phone systems that need expensive hardware, such as PBX systems, VoIP functions via existing internet connections, reducing the need for significant infrastructure investments. This makes it especially appealing to organizations seeking to reduce their overhead expenditures.
2️⃣ Enhanced Features and Flexibility
Rich Functionality: VoIP systems frequently provide advanced ways to communicate like as video conferencing, voicemail-to-email, call forwarding, and CRM integration. These services are usually not available on standard phone systems or demand an additional price.
Mobility and Scalability: With VoIP, users may make and receive calls from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility is useful for remote work and enterprises with numerous locations because adding more users or lines is simple and does not need physical setups.
3️⃣ Improved Call Quality
High-Quality Audio: When used with a stable internet connection, VoIP may give clearer audio quality than traditional phone lines. Modern VoIP systems use modern codecs and noise-canceling technology to improve audio quality. As internet speeds have increased, many users now enjoy low latency and jitter during conversations, making VoIP an appealing choice for high-quality communication.
Disadvantages of VoIP
1️⃣ Dependence on Internet Connectivity
Internet Reliability Is Required: For VoIP to work properly, it must have a steady and fast internet connection. Poor connection can cause lost calls, delays, and garbled audio. Users in places with intermittent internet connectivity may find VoIP inconvenient or annoying.
Bandwidth Limitations: When numerous users make calls on a restricted bandwidth connection, call quality suffers considerably. Organizations must provide enough bandwidth to meet their communication demands without disruptions.
2️⃣ Emergency Call Limitations
Location Tracking Issues: Unlike traditional landlines, which offer exact location information for emergency services, VoIP calls may not precisely communicate the caller’s position to emergency personnel. While some VoIP providers provide enhanced 911 (E911) services to help solve this issue, there are still limits as compared to traditional phone systems.
3️⃣ Potential Security Risks
Vulnerability to Cyber Threats: VoIP systems are vulnerable to cyber risks such as hacking and eavesdropping if not adequately protected. Calls transmitted over the internet can be intercepted by attackers unless encryption techniques are used. Businesses must establish strong security procedures to safeguard critical communications.
In a nutshell, while VoIP has significant benefits such as cost savings, additional capabilities, and improved call quality, it also has drawbacks such as internet reliance, emergency service limits, and possible security threats. Users should carefully evaluate these concerns before switching to VoIP technology.
VoIP Cost Structure Breakdown for Businesses
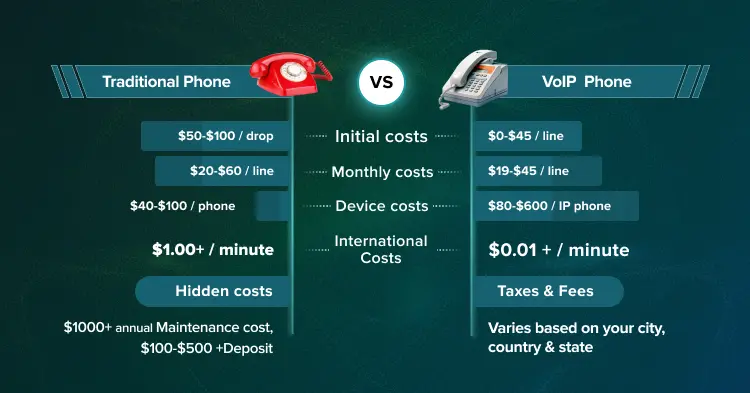
Want to know how much this amazing technology costs? These tables provide a comprehensive breakdown of VoIP costs across different business scenarios.
1. Initial Setup and Hardware Costs
| Component | Cost Range | Notes |
| IP Phones | $80 – $600/unit | Varies by model and features |
| Initial Setup Fee | $0 – $60/line | One-time implementation cost |
| Network Assessment | $200 – $600 | Optional but recommended |
| Router/Switch Upgrade | $200 – $1,000 | If needed for QoS support |
| Training | $0 – $200/session | Often included with service |
2. Monthly Service Costs
| Service Level | Cost Per User | Features Included |
| Basic | $19 – $25 | Voice calls – Voicemail – Basic features |
| Standard | $25 – $35 | Video calls – Mobile app – CRM integration |
| Premium | $35 – $45 | Advanced analytics – Call recording- API access |
3. International Calling Rates
| Region | VoIP Rate/Min | Traditional Rate/Min |
| North America | $0.01 – $0.05 | $0.50 – $1.00 |
| Europe | $0.02 – $0.10 | $1.00 – $2.00 |
| Asia | $0.03 – $0.15 | $1.50 – $3.00 |
| Other Regions | $0.05 – $0.20 | $2.00 – $4.00 |
4. Cost Comparison by Business Size (Monthly)
| Business Size | Users | VoIP Cost Range | Traditional Phone Cost |
| Small Business | 45432 | $250 – $900 | $500 – $2,000 |
| Medium Business | 21-100 | $800 – $3,500 | $2,000 – $8,000 |
| Large Business | 101-500 | $3,000 – $15,000 | $8,000 – $40,000 |
| Enterprise | 500+ | Custom Pricing | Custom Pricing |
5. Additional Costs and Fees
| Fee Type | Typical Cost Range | Frequency |
| E911 Service | $1 – $3/line | Monthly |
| Regulatory Fees | $2 – $5/line | Monthly |
| Number Porting | $0 – $30/number | One-time |
| Additional Virtual Numbers | $5 – $10/number | Monthly |
6. Traditional Phone System Hidden Costs (Not Present in VoIP)
| Cost Type | Typical Range | Frequency |
| Installation Fee | $50 – $100/drop | One-time |
| Security Deposit | $100 – $500 | One-time |
| Maintenance Contract | $1,000+ | Annual |
| Hardware Replacement | $500 – $2,000 | Every 5-7 years |
| System Upgrades | $1,000 – $5,000 | Every 3-5 years |
7. ROI Comparison (5-Year Projection for 50 Users)
| System Type | Initial Cost | 5-Year Total Cost | Estimated Savings |
| Traditional PBX | $20,000 – $30,000 | $120,000 – $150,000 | Baseline |
| Hosted VoIP | $5,000 – $10,000 | $60,000 – $80,000 | $40,000 – $70,000 |
Note: These are common estimates of how VoIP usually costs around businesses, and in different scenarios. The information provided above is purely for giving you an idea of how much likely you’ll pay for the technology and not a tentative cost.
Recommended Reading
How to Choose a VoIP provider
When assessing and selecting a VoIP service, running a background check is essential to ensure the solution aligns with your business’s needs. We’ve prepared this checklist to make things simple, easy and quick for you, when selecting a VoIP provider
1. Implementation Experience
- Provider offers comprehensive onboarding and configuration support
- Ability to set up advanced VoIP features like auto attendants, call queues, and call routing
- Proven track record of successfully deploying physical VoIP handsets
- Provides thorough user training and adoption guidance
2. Customization
- Provider offers complete customization options to personalize the VoIP experience for users
- Give full control over user data, without any third party intervention.
- Offers the solution at a cost customizable for your budget, while balancing your needs.
3. White-labeling
- Allows businesses to add their own company logo, colors and brand elements.
- Does not mention its name anywhere on the platform.
4. Network Compatibility
- VoIP solution is compatible with your existing network infrastructure
- Provider can customize the VoIP setup to seamlessly integrate with your network
- Ability to address any network bandwidth, quality of service (QoS), or security requirements
5. Industry-Specific Expertise
- Provider has experience working with companies in your industry
- Ability to understand and address the unique communication needs of your business sector
- Proven case studies or success stories with similar organizations
6. Customer Support Quality
- Provider offers 24/7 or rapid response customer support
- Responsive troubleshooting and issue resolution for tasks like number porting
- Availability of on-site or remote technical support for implementation and ongoing maintenance
7. High Availability and Security
- Provider guarantees high uptime and reliability, such as 99.999% uptime
- Comprehensive 24/7 network monitoring and proactive issue resolution
- Data centers and infrastructure that meet rigorous security standards (e.g., ISO/IEC 27001 certification)
- Robust security measures, including encryption, authentication, and access controls
8. Features and Capabilities
- A robust VoIP API solution offers the essential features your business requires, such as:
- Unified communications (voice, video, messaging, collaboration)
- Mobility and remote work support
- Integrations with CRM, productivity, and other business applications
- Ability to scale the VoIP system as your business grows
9. Cost-Effectiveness
- Transparent and competitive pricing structure
- Consideration of initial setup costs, monthly service fees, and long-term total cost of ownership
- Potential for cost savings compared to traditional phone systems
10. Reputation and References
- Provider has a strong industry reputation and positive customer reviews
- Availability of references or case studies from similar businesses
- Financial stability and longevity of the VoIP provider
MirrorFly: A VoIP Provider You Should Not Miss

You might wonder if there are any solutions out there that lets you tick all of the above curated criteria. Let me tell you – MirrorFly is a fantastic option for the following reasons:
MirrorFly stands out as the finest VoIP option for organizations because of its extensive and customized communication platform, which effortlessly integrates audio, video, and chat capabilities across several devices. MirrorFly enables businesses to efficiently improve customer interaction and collaboration by providing over 1000+ features such as high-quality audio and video conferencing, in-app chat, and sophisticated call management capabilities.
You can customize the security features as much as you want, while its in-built security features such as end-to-end encryption guarantee that conversations are private and safe, defending your platform from attackers.
Furthermore, MirrorFly’s deployment flexibility, which includes both cloud-hosted and self-managed alternatives, allows organizations to grow their communication solutions to meet their individual requirements without sacrificing performance or security.
Overall, MirrorFly’s mix of functionality, scalability, and security makes it an excellent solution for enterprises trying to improve their communication methods.
Impressed? You can check out the solution here or contact the team and discuss how you can implement your VoIP platform with MirrorFly right from here.
Got more questions? Write down in the comments below and we’d be more than happy to help you on this!
Looking to Build Your Voice Chat App
Get our enterprise-grade communication solution, that can be set up on your company servers.
Contact Sales100% customizable
White-label solution
Full source code

Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a VoIP calling?
VoIP calling is a type of phone calling established using the Voice over Internet Protocol technology that allows you to make voice calls using an internet connection instead of a traditional phone line.
What does VoIP stand for?
VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. It is the technology of making phone calls through the internet instead of regular phone lines. It turns voice signals into digital data that travels over the internet to reach the person you’re calling.
What are the benefits of using VoIP?
The benefits of using VoIP include:
– Lower costs compared to traditional phone lines
– Easy scalability to add or remove users
– Portability to make calls from any internet-connected device
– Advanced features like call forwarding and voicemail transcription
– Better voice quality
– Integration with other business applications
– Flexibility through softphone applications
– Enhanced security through encryption
– Simple conference calling capabilities
How does VoIP work step-by-step?
Voice to Digital Signal: Your voice is converted into digital data by an analog-to-digital converter in your device.
Packet Creation: This digital signal is divided into small data packets with destination information.
Transmission via Router: These packets are sent through your internet router.
Internet Delivery: The packets travel over the internet to reach the recipient.
Packet Reassembly: At the destination, the packets are put back together in the correct order.
Digital to Analog Conversion: The digital signal is converted back to an analog audio signal so the recipient can hear your voice.
Can a VoIP phone be used as a regular phone?
Yes, a VoIP phone can be used as a regular phone. It allows you to make and receive calls just like a traditional phone, but it works over the internet instead of phone lines. You’ll need a stable internet connection to use it effectively. VoIP phones typically offer additional features that regular phones don’t have, such as enhanced call forwarding and digital voicemail.
Do I need a VoIP phone to use VoIP?
No, you don’t necessarily need a dedicated VoIP phone to use VoIP. You can use:
– Regular phone with a VoIP adapter
– Computer with VoIP software
– Mobile phone with a VoIP app (softphone)
The essential requirements are a VoIP service provider and a reliable internet connection.
Related Articles




can you explain me Is a high-speed internet connection required for VoIP calls?
Of course Stella we pleasure to tell you
steady and dependable web association is pivotal for quality VoIP calls. A high velocity broadband association with adequate transfer speed is prescribed to guarantee clear and continuous calls.
What are some popular VoIP service providers?
This is from my side the popular Service providers in 2023, I hope it may helpful to you to discover something better.
Skype
Google Voice
Zoom
RingCentral
Vonage
Keep in mind that the availability and popularity of service providers might have changed since then.
Hello team,
The article was well-written, Can I use my existing phone for VoIP calls?
Hello,
I think there is lot of probabilities to do as your question In some cases, you can use your existing phone with an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) to convert analog signals to digital signals compatible with VoIP technology. However, dedicated VoIP phones offer better functionality and performance. for your more clarification about VoIP you can free to call us.
Hi,
Nice article, what kind of advantages I can get by using a VoIP phone?
Hi,
I just went through your article, it was quite nice also I have a query that Can I use VoIP phone as a regular phone?
Greetings Rajeshpat! Thanks for your compliment on my blog. Yes, obviously, you can use your VoIP phone as a regular phone. VoIP phones often resemble the appearance and functionality of a traditional phone. VoIP is an additional service that allows you to make and receive calls over the internet. Hence, you can switch your phone from VoIP to a traditional phone or vice versa. But make sure your phone provider offers you VoIP capabilities, and register with a VoIP provider to switch instantly based on your comfort.
Hello,
What is the difference between phone and VoIP?
Hello Anikha,
The primary difference between a phone and VoIP is the technology used to transmit voice communications. Such as phones use analogue transmission and VoIP uses digital transmission, Which makes VoIP communication cost-effective, highly scalable, and offers more features that can fix communication barriers in any business.
Hi team,
Nice article, here I have a doubt kindly clear me if possible, What kind of providers offers voip phones?
Thanks John! ,
Sure, my existence and purpose over here are to clarify your queries. There are various kinds of providers that offer VoIP phones, such as Ringcentral, 8×8, Vonage, Nextiva, Jive, Grasshopper, Dialpad, Ooma, etc. You can choose any of these providers that fit your business needs. Or if you require more details on VoIP and customizable in-app VoIP communication providers, then you can contact MirrorFly experts onboard.